Containers and Kubernetes
Questions:
- Running Kubernetes on vm only without cloud providers?
Develop Kubernetes enabled applications. Skafold
- What is kubernetes? (Short form - k8s)
- scale up the system
- orchestration tool
- orchestrate dockerized applications
more effective use of servers / space
- What is kubernetes cluster? *
What is cloud native application?
- Kubernetes vs docker
“Desired State Management”
Containers
- It needs to be managed.
- Networking is definitely hard.
- Containers must be scheduled, distributed and load balanced.
- And the data’s got to be persisted somewhere.
Kubernetes
- “Kubernetes” greek word for captain or pilot of the ship.
- running 1000 of containers on production
- not tied to a specific cloud provider
- manage resources on the cloud
if a container goes down, another container gets started, handled by a sweet system (kubernetes)
- Kubernetes uses
labelsas “nametags” to identify things and it can query based on these labels
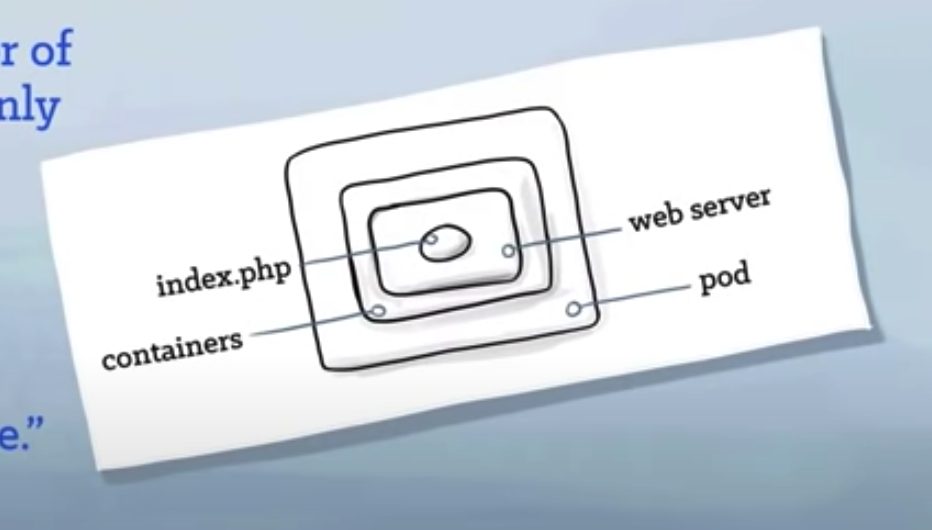
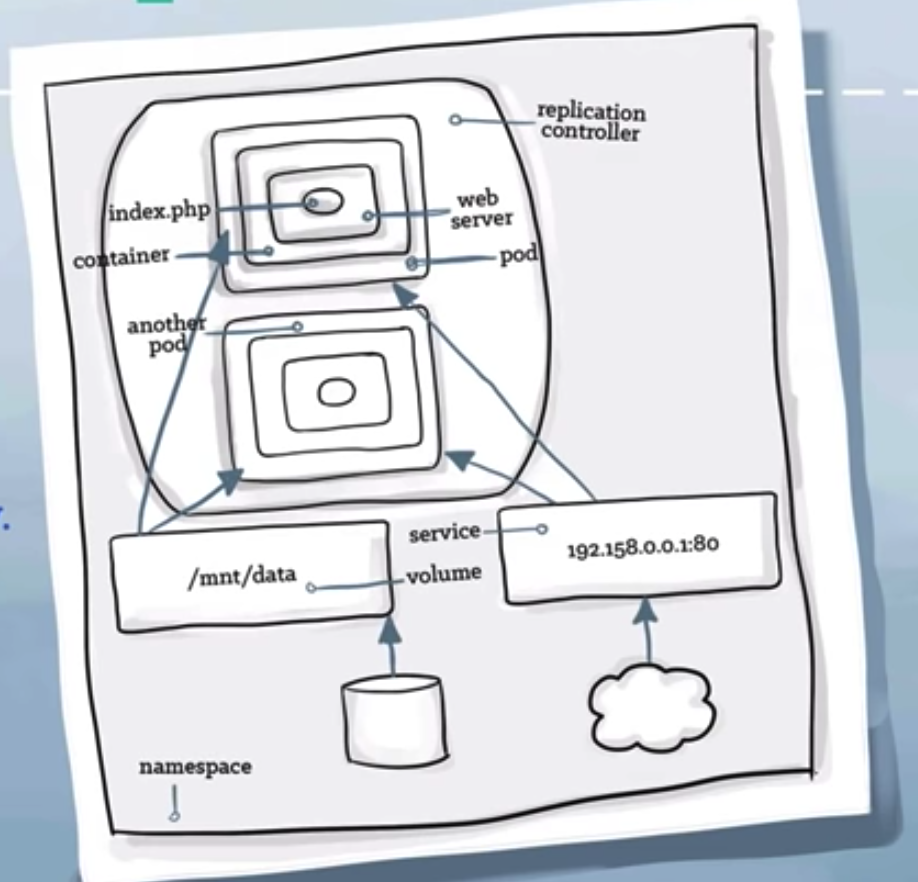
Kubernetes - PODS
- a runnable unit of work
- generally, we use only one container per pod.
- a pod can hold any number of containers, but usually it only holds two (tightly coupled containers).
- a pod is connected via an overlay network to the rest of the environment.
- Kubernetes (works for us) by connecting the pods to the network and rest of the kubernets ecosystem.
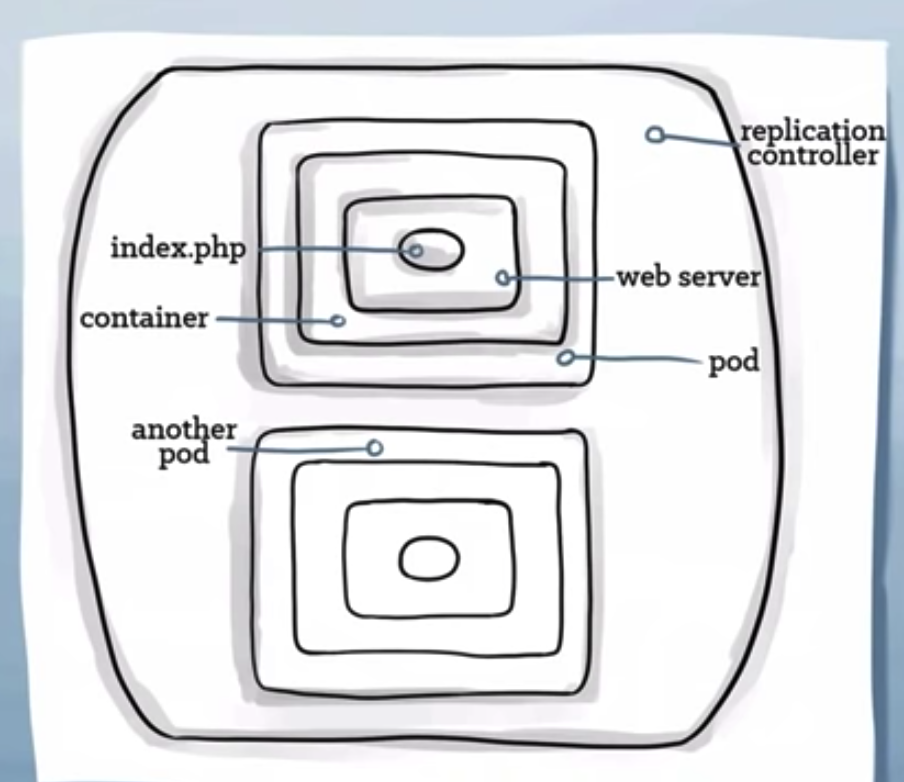
Kubernetes - Replication Controllers
- for managing any arbitrary(random) number of pods
Pod Template
- for creating any number of pod copies, as much as necessary when scaling.
Provides logic for scaling the pod up or down
Through the Replication controllers, kubernetes will manage pod lifecycle, scaling up and down, rolling deployments and monitoring.
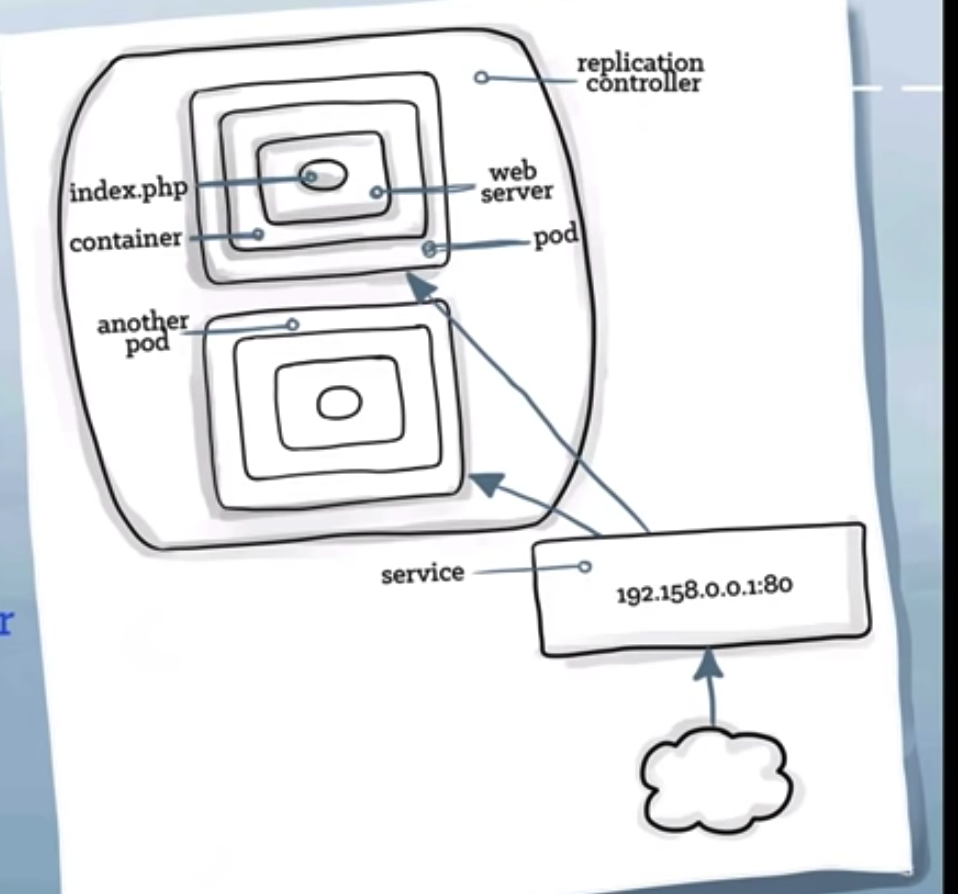
Kubernetes services
- tells the rest of kubernetes environment(pods and replication controllers) what services application provides.
- pods may come and go but ip addr and ports remain the same.
- other service can find our service through kubernetes service discovery
- it is persistent.
- provides discovery.
- load balances
- provides VIP layer
??? - identifies pods by label selector
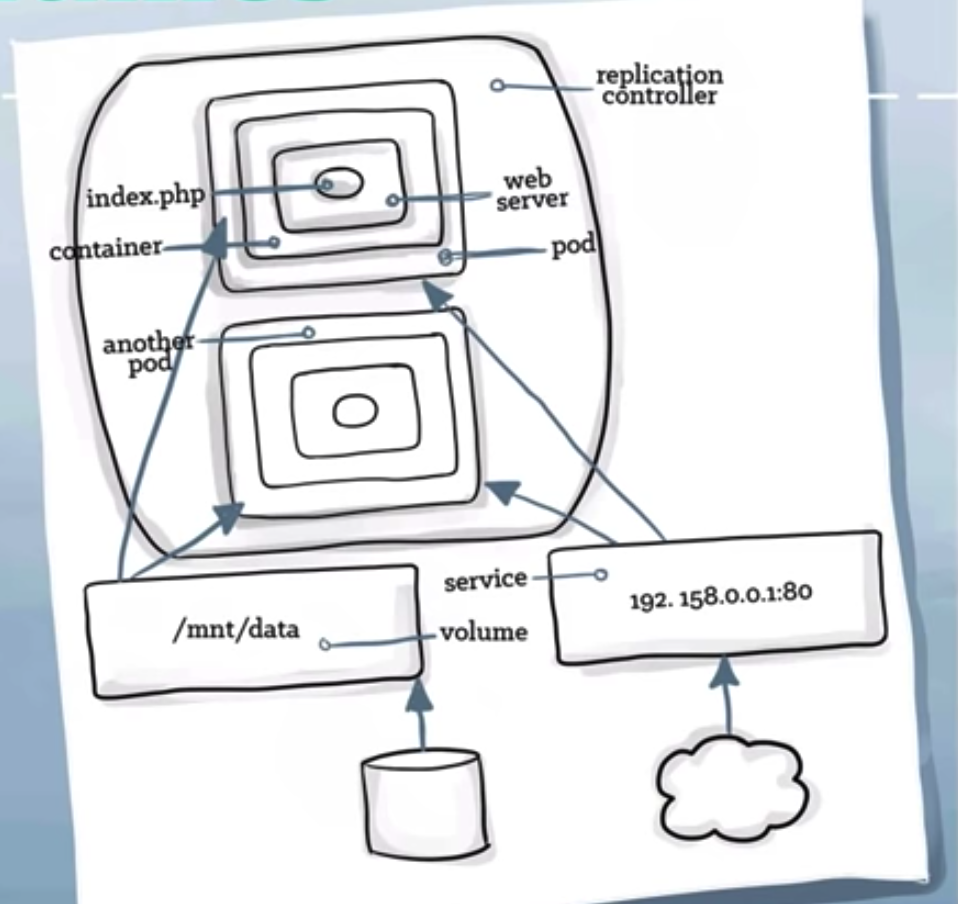
Kubernetes - Volumes
- location where containers can access or store information
- for application volume is local file system
volumes maybe backed by storage backends such as: ceph, gluster(red hat), Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS)
Kubernetes - Namespace
What is namespace?
- organizing resources in namespace
- virtual cluster inside a cluster
Namespaces
Minikube
- minikube comes with
kubernetes-dashboardnamespace which is not provided on standard cluster.
kube-system (namespace)
- dont’ modify
kube-public
Kubernetes
- 4 Namespaces Default
- grouping mechanism inside kubernetes
- services, pods, repliaction controllers and volumes could easily co-operate within a namespace
Nodes
- maybe a vm or physical machine depending on the cluster
- has the services necessary to run application containers
Kubernetes - HELM
What is Helm?
- package manager for kubernetes
- to package yaml files and distribute them to public / private repositories
The package manager for Kubernetes: tool for installing, upgrading and managing applications on a Kubernetes cluster.
Helm Packages (Charts)
- describes how we install packages onto a Kubernetes cluster.
helm has two parts
| A Client (Helm) | A Server (Tiler) |
|---|---|
local helm client sends instructions to tiller in the cluster | runs inside of kubernetes cluster |
- install helm
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/helm/master/scripts/get | bash
helm installed into /usr/local/bin/helm tiller installed into /usr/local/bin/tiller Run 'helm init' to configure helm.
Best Practices
Namespaces
- virtual cluster within a cluster
Kubernetes cluster has 3 namespaces by default:
- default (all the default goes here)
- kube-system (no need to touch it)
kube-public (leave it alone)
- display all namespaces
$ kubens
- switch to namespace
$ kubens test
different teams should be using different namespaces:
- codehub-prod
codehub-dev
- fuse-ai-prod
- fuse-ai-dev
istio
- cross communication using
- Connect, secure, control, and observe services.
spinnaker
- Cloud Native Continuous Delivery Fast, safe, repeatable deployments for every Enterprise
Kubernetes Concepts
What is Kubernetes?
1
Kubernetes is a production-grade, open-source platform that orchestrates the placement (scheduling) and execution of application containers within and across computer clusters.
- Kubernetes automates the distribution and scheduling of application containers across a cluster in a more efficient way.
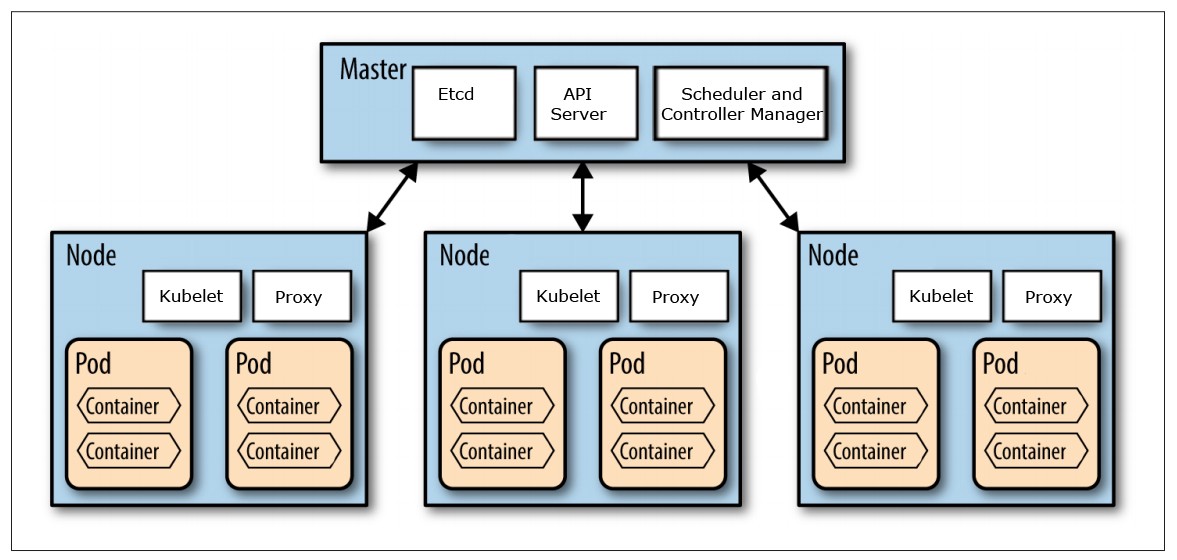
What are Kubernetes Clusters?
A Kubernetes cluster consists of two types of resources:
- master
- The master coordinates the cluster.
- node
- Nodes are the workers that run applications.
Masters
1
Masters manage the cluster and the nodes that are used to host the running applications.
- responsible for managing the cluster.
- etcd -> single source of truth regarding the key value pairs of pods information on kubernetes cluster.
- scheduler / controller as same as their name suggests.
Node
1
A node is a VM or a physical computer that serves as a `worker machine` in a Kubernetes cluster.
- Each node consists of:
- kubelet
- kube proxy
- a container runtime, responsible for pulling the container image, unpacking and running on a machine.
- managed by
The Master
- A
Nodecan have multiple pods.
A Kubernetes cluster that handles production traffic should have a minimum of three nodes.
Kubernetes Deployment (Application Management)
1
Deployment instructs Kubernetes how to create and update instances of our application and ***responsible for creating and updating instances of our application***
- need to specify the container image for our application.
- need to specify the the number of replicas that we want to run.
Kubernetes master schedules the application instances included in the Deployment to run on individual Nodes in the cluster.
Deployment Controller
- continously monitors application instances
Self Healing Mechanism
- If the
NODEhosting an instance goes down or is deleted, theDeployment controllerreplaces the instance with an instance on anotherNODEin the cluster.
Applications need to be packaged into one of the supported container formats in order to be deployed on Kubernetes
Pods
1
A Pod is a group of one or more application containers (such as Docker or rkt) and includes shared storage (volumes), IP address and information about how to run them.
- can contain different different application containers.
- Pods are the atomic unit on the Kubernetes platform.
- When we create a Deployment on Kubernetes, that Deployment creates Pods with containers inside them (as opposed to creating containers directly)
Pods are
mortal- In case of Node
failure, identical pods are scheduled on other availableNodesin the cluster.
Kubernetes Services
1
A Service in Kubernetes is an abstraction which defines a logical set of Pods and a policy by which to access them.
- Although each Pod has a unique IP address, those IPs are not exposed outside the cluster without a
Service. - Services allow our applications to receive traffic.
- A Service routes traffic across a set of Pods.
$ kubectl expose deployment hello-node --type=LoadBalancer --port=8080
Services can be exposed in different ways by specifying a type in the ServiceSpec:
| Cluster IP(default) | NodePort | Load Balancer | External Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exposes the Service on an internal IP in the cluster. | Exposes the Service on the same port of each selected Node in the cluster using NAT. Makes a Service accessible from outside the cluster using | Creates an external load balancer in the current cloud (if supported) and assigns a fixed, external IP to the Service. | Exposes the Service using an arbitrary name (specified by externalName in the spec) by returning a CNAME record with the name. |
Kubernetes ReplicaSet
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/controllers/replicaset/
Kubernetes Labels and Selectors
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/labels/
Kubernetes Manifest
Manifests are a way to declaratively define our microservice.
Kubectl
1
Kubectl uses the Kubernetes API to interact with the cluster
$ kubectl get- list resources$ kubectl describe- show detailed information about a resource$ kubectl logs- print the logs from a container in a pod$ kubectl exec- execute a command on a container in a pod
Kubernetes Scaling
When traffic increases, we will need to scale the application to keep up with user demand.
- Scaling is accomplished by changing the number of replicas in a Deployment
References
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tutorials/ https://kubernetes.io/docs/tutorials/kubernetes-basics/scale/scale-intro/
Kubernetes Configuration (YAML Cheats)
- every configuration consists of 3 different parts:
- metadata
- specification (specs)
DESIRED STATE - status (automatically generated by k8s)
Actual State- k8s maintains status from the kubernetes master
etcd
- k8s maintains status from the kubernetes master
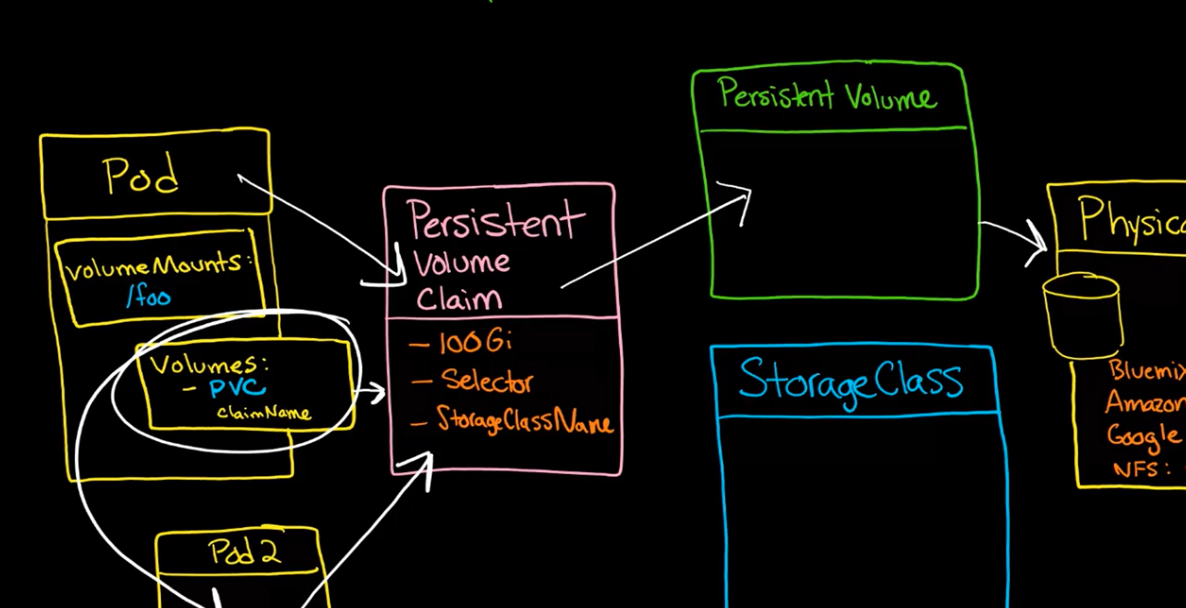
Persistent Volumes
Why PV?
- because of multiple storage architectures
- one storage interface to deal with different storage solution
Storage Infrastructure
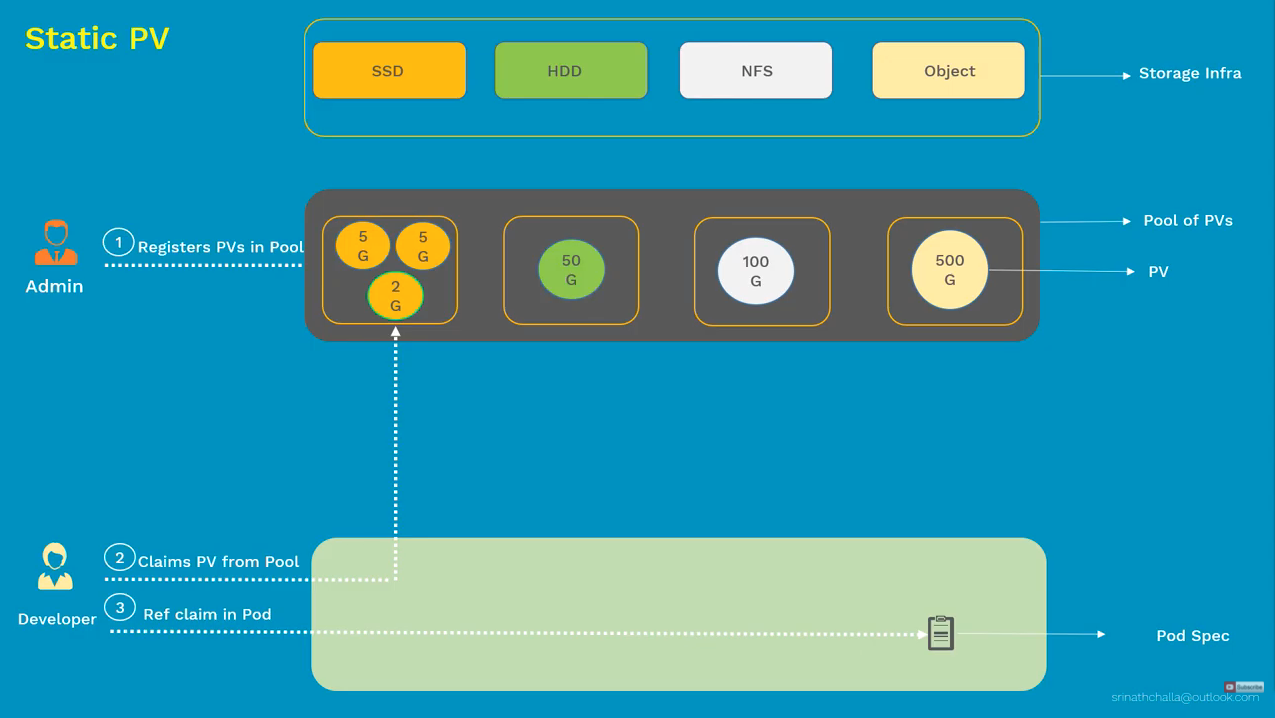
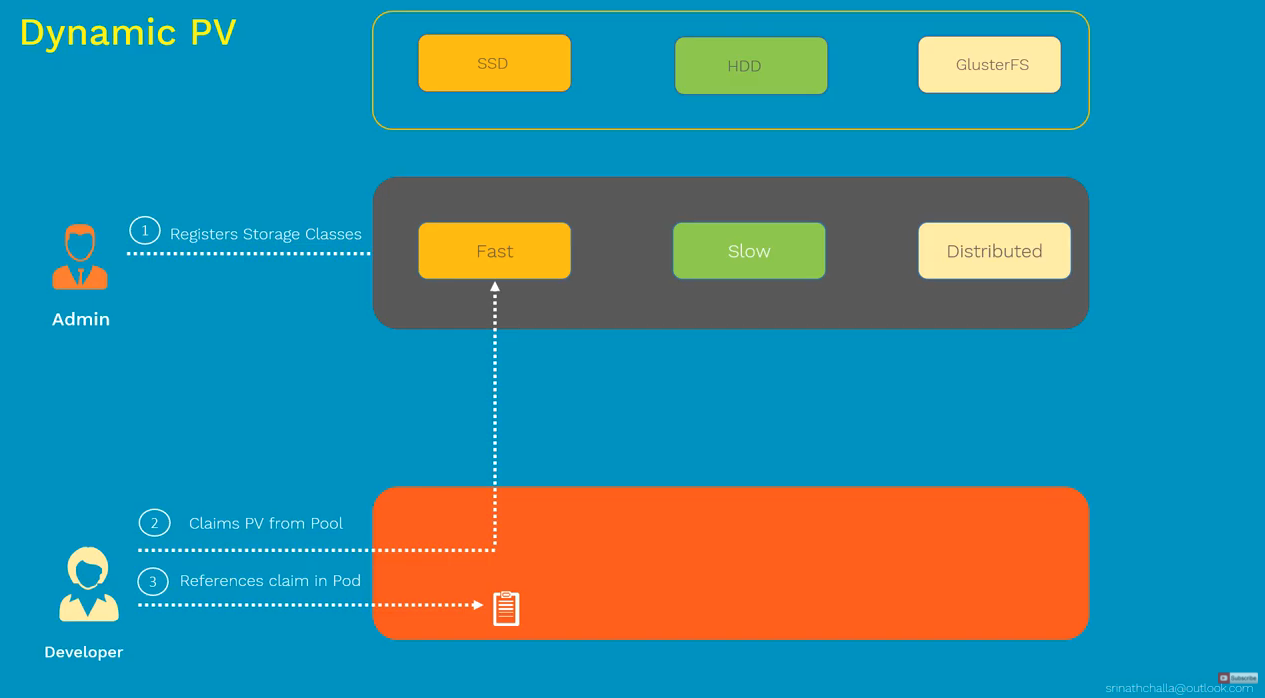
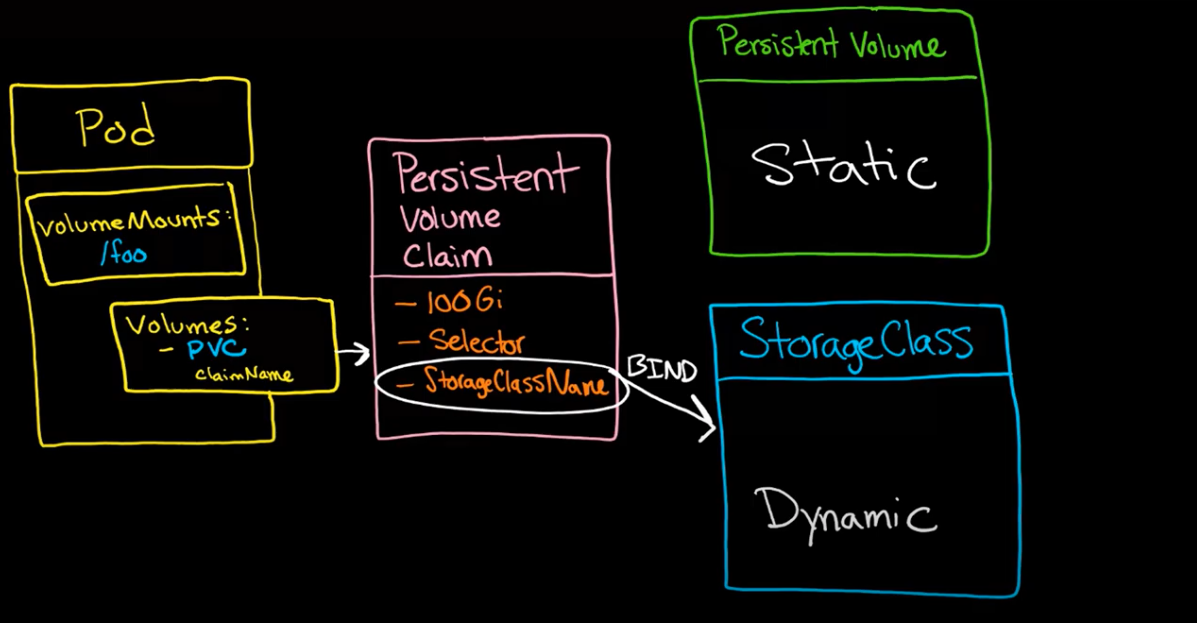
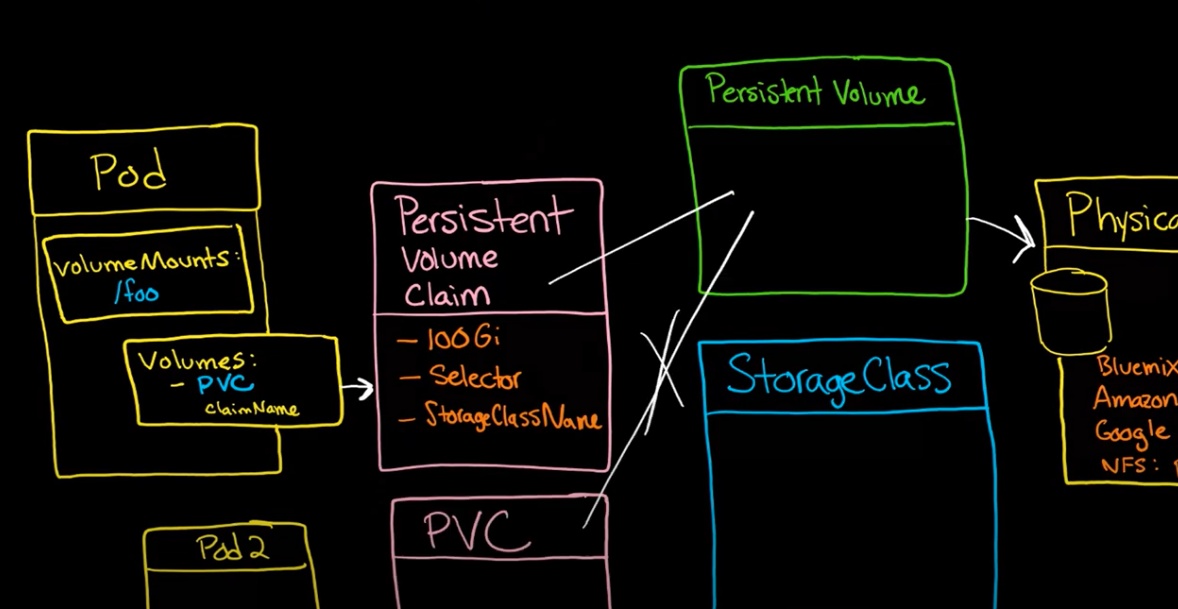
Persistent Volume (PV)
- piece of storage in cluster (administrators)
Persistent Volume Claim (PVC)
- request for storage (developers)
Access modes
- read / write
- read only
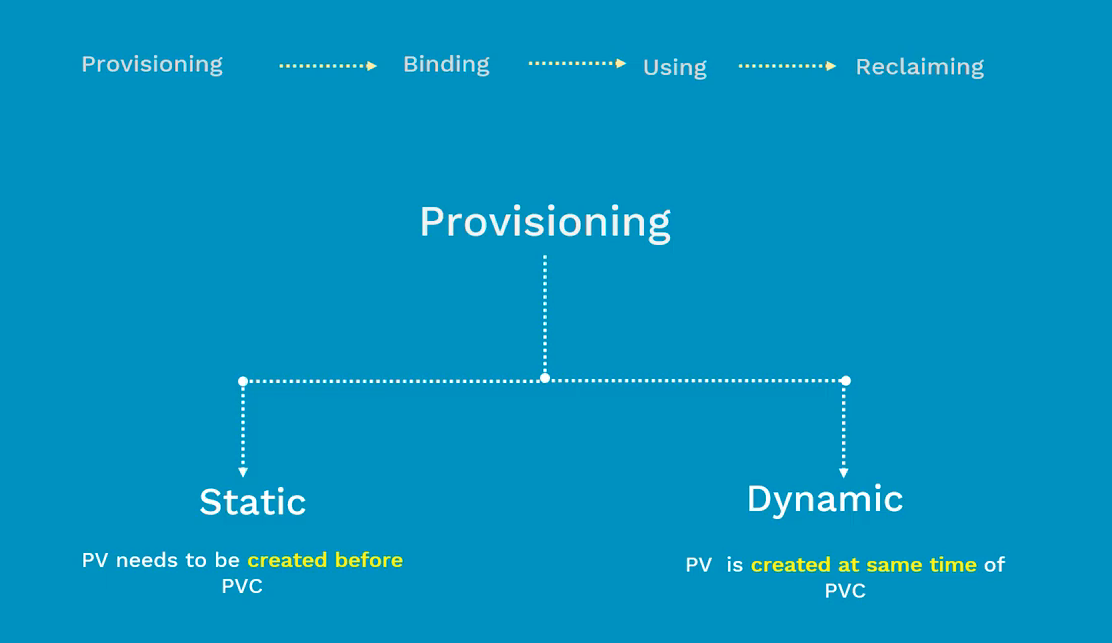
Lifecycle of PV
Static PV
Dynamic PV
Binding
- pvc pointing to pv or a storage class = binding